Just Earth News | @justearthnews | 16 Aug 2024, 07:36 am Print
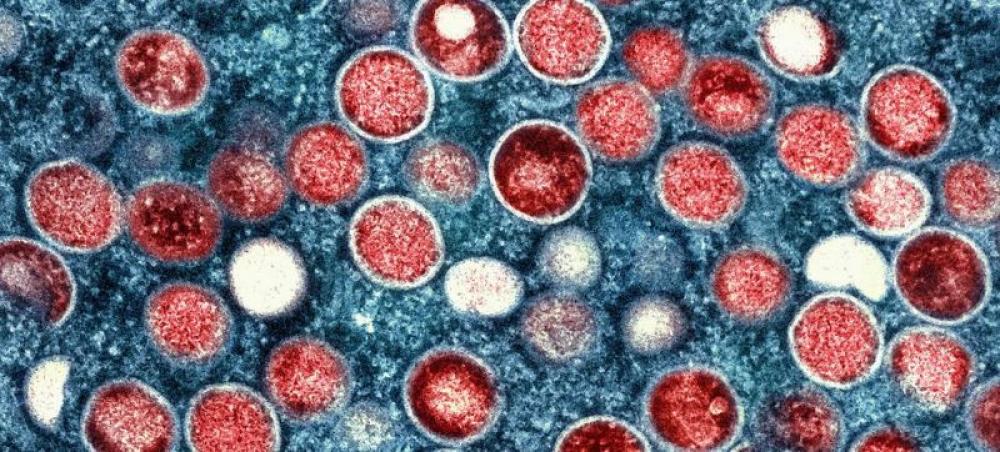
Photo Courtesy: NIAID
Pakistan has registered three mpox cases, a disease which has now been described by the World Health Organisation as an international global health emergency.
In a press statement issued here on Friday, said Director Public Health Dr. Irshad Ahmad Roghani said the Health Department is establishing isolation wards for Mpox patients while COVID teams have been made functional at their stations of duty, reported ARY News.
“Contact tracing of suspected patients is also in progress to detect further spread of the disease,” he said.
The World Health Organization (WHO) is supporting African countries to scale up response to curb mpox.
The outbreak that affected the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and spread to neighbouring countries continues to grow.
On Thursday afternoon, WHO member Sweden became the first country outside Africa to record a case of the mpox Clade 1 variant that is believed to be driving the latest outbreak.
“We are hard at work on the frontlines of the response, collaborating closely with governments and communities to strengthen mpox control measures and are ramping up efforts to curb the widening trend of the virus through coordinated action with partners and national authorities,” said Dr. Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa.
Viral disease, global concern
Mpox – formerly monkeypox - is a viral disease that can be transmitted through physical contact with an infected person, animal or contaminated objects.
It was first detected in humans in 1970, in the DRC, and is considered endemic to countries in Central and West Africa.
Outbreaks are caused by different mpox viruses called clades, and the clade 1 strain has been circulating in the DRC for years.
The emergence of a new offshoot – clade 1b - and its rapid spread, including to nearby countries, is among the main reasons why WHO declared on Wednesday that mpox constitutes a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC).
So far this year, more than 2,100 laboratory confirmed cases of the disease, and 13 deaths, have been reported in the DRC and 11 other countries: Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Kenya, Liberia, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Africa and Uganda.
This compares to 1,145 confirmed cases, and seven deaths, in 11 countries for all of 2023.
Support and collaboration
WHO is stepping up support to the affected countries by deploying additional experts, including epidemiologists and anthropologists, and providing initial funding to accelerate outbreak response measures.
Efforts are underway to enhance cross-border collaboration for case investigation, contact tracing and community engagement to ensure compliance with preventive measures.
The UN agency is also assisting national regulatory authorities to speed up regulatory approvals, as well as providing guidance to national immunization technical advisory groups to ensure readiness for vaccine rollout.
- Ukraine’s health system under fire: Attacks spike 20% in 2025, WHO warns
- A dog’s loving lick turned deadly — She woke up without her limbs
- Scientists reveal how exercise could protect your brain from Alzheimer’s
- The cure exists — So why are Cataract patients still going blind?
- New hybrid Mpox strain surfaces in UK and India — WHO sounds global alert




-1763561110.jpg)
