Just Earth News | @justearthnews | 07 Oct 2024
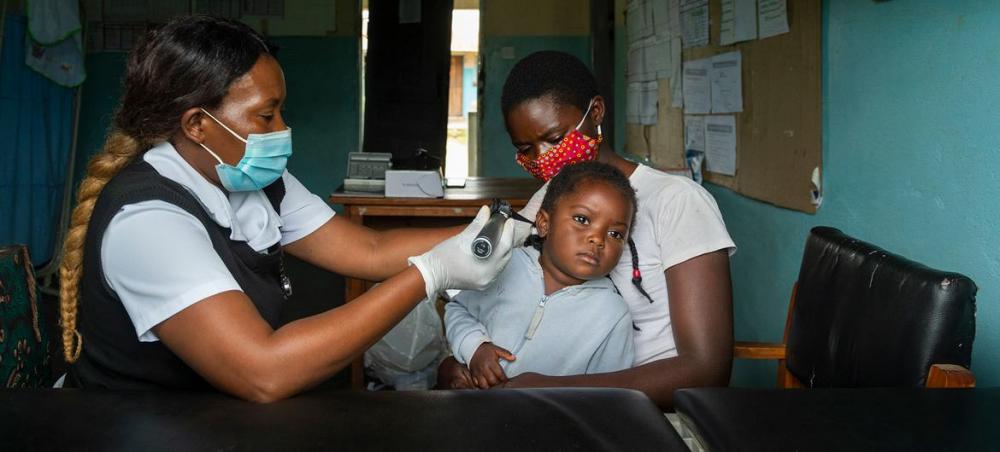
Ear and hearing care in a clinic in Zambia. Photo Courtesy: WHO/Blink Media/Gareth Bentley
The number of people in Africa living with hearing loss could rise to 54 million by 2030, up from 40 million today, unless urgent measures are taken, the World Health Organization (WHO) said in a report published on Monday.
Hearing loss already costs the continent $27 million annually, exacting profound impact on lives and economies, according to the report, which was launched at the African Summit on Hearing Impairment in Nairobi, Kenya.
Widespread hearing loss disproportionately affects poor and vulnerable populations. WHO warned that without urgent interventions it will continue to escalate, amplifying existing inequalities in access to health services.
Children at a loss
The UN agency said hearing loss has far-reaching consequences for children, including delays in language development, thus increasing the risk of poor educational outcomes and limited career prospects in the future.
Meanwhile, adults with untreated hearing loss often face isolation, loneliness and increased risk of depression and dementia.
The report details numerous factors driving the surge in hearing loss in WHO’s Africa Region which covers 47 countries. Chief among them is the acute shortage of ear and hearing care (EHC) specialists as well as uneven distribution of the available workforce, which is mainly in urban areas.
Shortage of professionals
For example, more than 56 per cent of African countries have just a single ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist for every million people, whereas in Europe it is roughly 50 per million.
Meanwhile, more than three-quarters of countries have fewer than one audiologist and one speech and language therapist for every million people.
And although 33 million Africans could benefit from a hearing aid, only around 10 per cent have access due to lack of EHC financing, and consequent high costs.
Newborn screening lacking
The report noted that among children living in low and middle-income countries, up to 75 per cent of hearing loss is due to preventable causes such as infections and common ear diseases as well as birth complications. Yet, most countries do not routinely conduct hearing screening of newborns.
Even in countries with EHC programmes, related interventions are not integrated into school and workplace health programmes, or healthy ageing programmes.
This challenge is further compounded by lack of national policies and plans for strengthening delivery of EHC, and low implementation even where they exist. Additionally, 35 per cent of countries do not have a budget allocated to EHC activities, meaning patients must bear the entire cost of treatment and care.
Advocacy, integration and financing
The report contains several recommendations. For example, countries should leverage the findings to galvanize action at the highest level, including advocating for policies focused on EHC and related activities.
EHC should also be urgently integrated into existing programmes to optimize use of scarce resources, while governments should explore public-private partnerships towards strengthening services.
The report also highlighted the need for dedicated financing for EHC, to equip facilities and deliver products and technologies, among other measures.