Just Earth News | @justearthnews | 13 Apr 2022
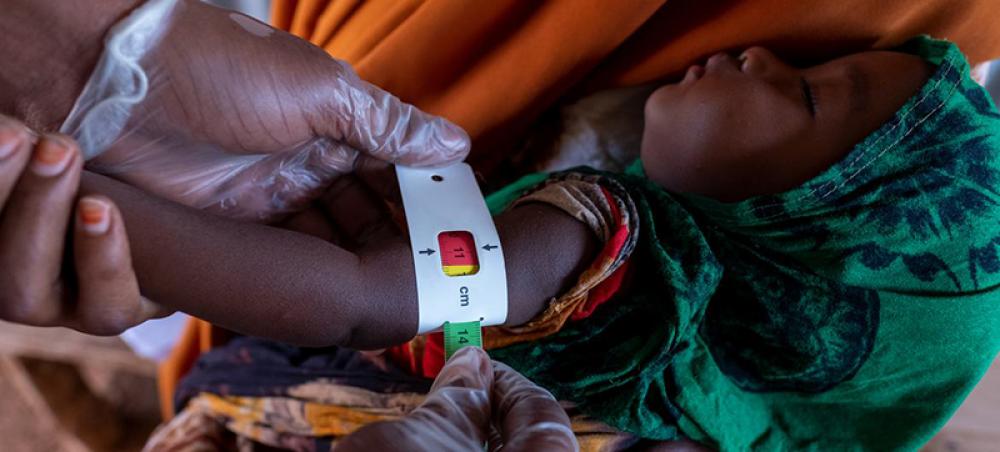
Image: UNICEF/Sebastian Rich
The threat of famine is very real in Somalia and South Sudan and urgent action is needed now to avoid a catastrophe, UN humanitarians warned on Tuesday.
The alert from the World Food Programme (WFP) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) followed the latest food security assessments which showed that six million people in Somalia will face acute food insecurity in the coming months, unless the rains come.
That is almost double the number at the start of the year, said Lara Fossi, WFP Deputy Country Director in Somalia, who noted that Somalia last endured famine in 2011 and only narrowly avoided it in 2016-2017, thanks to prompt humanitarian intervention.
“This is a heads-up that this assessment is showing that we are already identifying six areas in Somalia that are at risk of famine, that are at risk of going down that route of 2011 if we don't act now,” she said.
Record needs in South Sudan
The situation is equally devastating in South Sudan, where “two-thirds of the country will likely face hunger between May and July of this year,” said Meshack Malo, FAO Representative in South Sudan, speaking via Zoom from Juba. “In terms of actual numbers, that means this is about 7.74 million people; this is the highest number ever recorded.”
Famine was declared in two counties of South Sudan in 2017, although prompt international assistance prevented the situation from deteriorating further.
Citing the latest IPC data on food insecurity across South Sudan, Mr. Malo noted that 1.34 million children are “malnourished severely. And over 600,000 pregnant and lactating women are malnourished this year”.
Multiple risk factors
The drivers of chronic food insecurity in South Sudan include the civil war that started in 2013 and ended in 2020. It caused widespread destruction, death and displacement, leaving two million people internally displaced and another 2.3 million as refugees in neighbouring countries.
Some of the worst flooding in generations has also driven displacement and pushed local communities to breaking point, reducing crop production and dependence on imports which have undermined people’s ability to secure sufficient nutritious food all year round.
Displaced by failed rains
Back in Somalia, the devastating effects of successive failed rains have already pushed people to leave their homes in search of food and work.
“There are dozens of camps for the internally displaced people which have grown exponentially in the last few months,” said WFP’s Ms. Fossi, speaking via Zoom from Mogadishu.
“Thousands of households are pouring into them from the areas hardest-hit by the drought. They are desperately seeking assistance and when you visit some of these camps, you can see the lines of the new arrivals coming in and many of these people are women and children, and frankly, it's impossible to see them, and not be shocked by the visible signs of destitution and life-threatening malnutrition.”
Impossible choices
The WFP officer warned that the agency is now “taking from the hungry to feed the starving” as it struggles to scale up its emergency response to 2.5 million people in Somalia – “a next to impossible feat, considering our relief funding gap of $149 million”.
She added: “The latest data shows how rapidly things are getting worse, with six million people now facing acute food insecurity in the coming months. This is almost double the number at the start of the year.
“It's almost 40 per cent of the population and there is a real risk of famine in some areas if the current rainy season fails.”